[LeetCode] Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
문제 설명: Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth.
The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
1
2
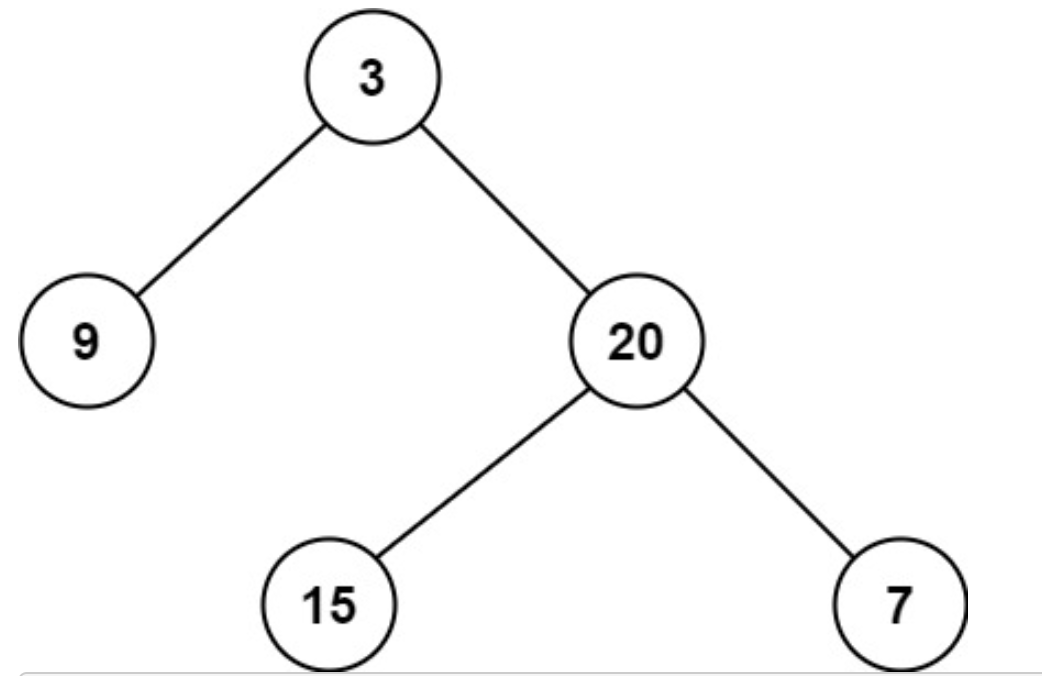
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 2
난이도: EASY
문제를 보고 처음한 생각
binary tree 문제이고, DFS를 통해 Sub Tree의 Leaf Node까지의 cost를 계산하고, 이 중에서 min() 함수를 통해 최소인 cost를 선택해준다면 된다고 생각하였다.
문제를 해결한 방법
_위의 주석은 LeetCode에서 제공하는 TreeNode 클래스이다. _
1
2
3
4
5
6
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
1
2
def minDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
return self.dfs(root)
minDepth 함수에서는 dfs함수를 호출하는데, 이 dfs 함수는 treeNode를 인자로 받는다.
여기서 몇 가지 조건 분기를 하는데, 조건들은 다음과 같다.
- 현재 node가 없는 경우
- 현재 node의 right child만 있는 경우
- 현재 node의 left child만 있는 경우
- 현재 node의 양쪽 child가 모두 있는 경우
위 조건들을 토대로 짠 전체 코드는 다음과 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
class Solution:
def dfs(self, node: TreeNode) -> int:
if node == None: # node가 없다면 return
return 0
if node.left == None: #만약 node의 left child가 없다면
return 1 + self.dfs(node.right) # right child로 dfs
elif node.right == None: #만약 node의 right child가 없다면
return 1 + self.dfs(node.left) # left child로 dfs
else:
# 양쪽 다 있으면 dfs(leftNode), dfs(rightNode)중 작은 것 선택
return 1 + min(self.dfs(node.left), self.dfs(node.right))
def minDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
return self.dfs(root)
dfs 함수는 반환 타입으로 int를 가지며, node가 없는 경우를 제외한 경우에선 dfs(next_node)와 1을 더해서 return 하는 방식으로 경로의 누적 cost를 계산하였다.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.